Automatically Enable CDC In RDS SQL Server
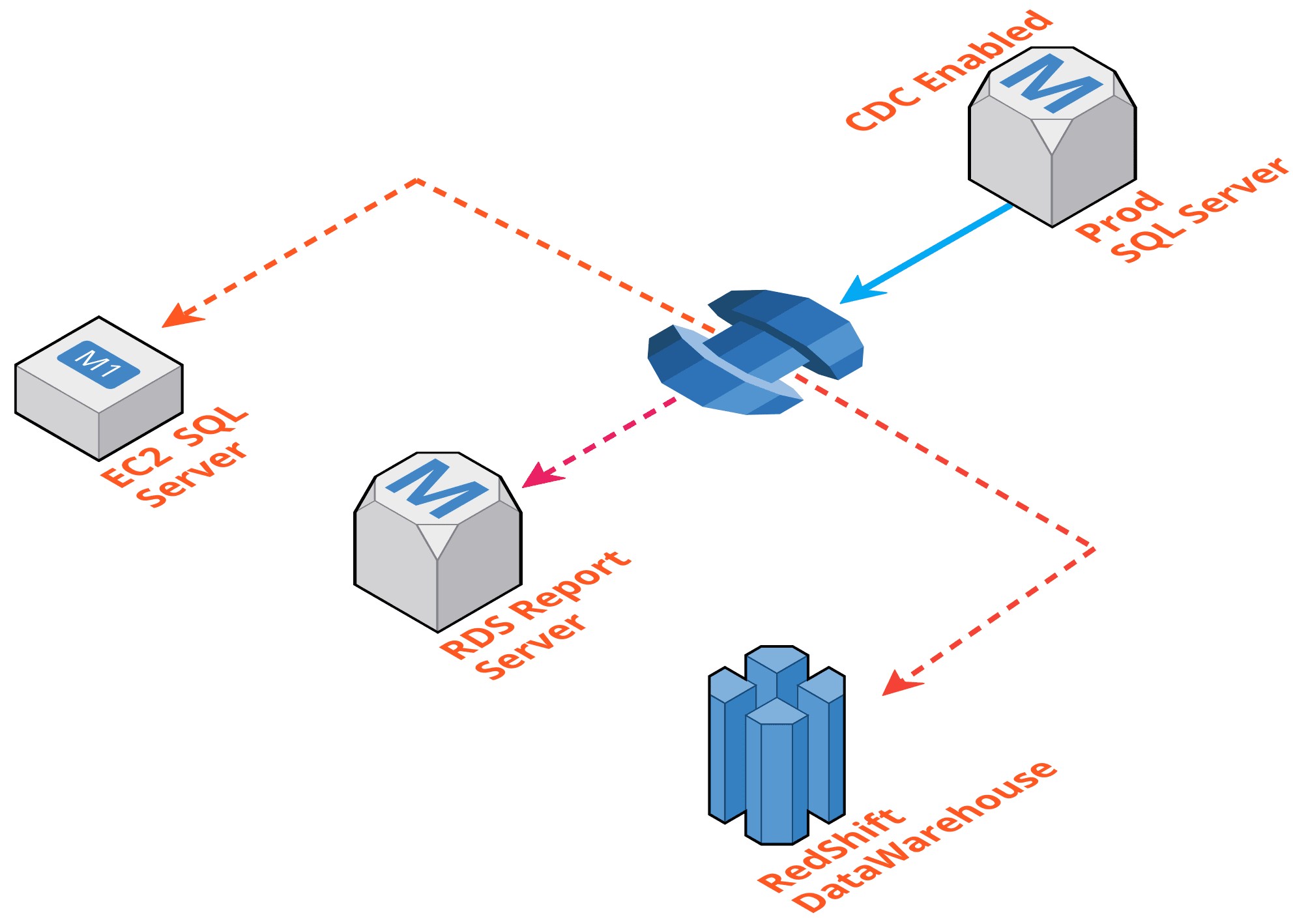
AWS recently announced a new feature which will help to enable CDC in RDS SQL server on user databases. Here this the detailed blog post that explains how to enable this CDC for DMS service. CDC is an enterprise edition feature. But RDS SQL Server Standard editions are supporting CDC. The most important thing is we can use this feature to achieve the below things.
- Reporting Server: Since the read replica is not supported for MSSQL and Oracle in RDS, so by using DMS ongoing replication we can make a real-time Reporting Server for this. Also you can replicate the data to any one of your data warehouse like RedShift.
- Cross Region DR: Inter-Region VPC peering is generally available now. So we can create a DR solution for your RDS SQL Server to another region.
Primary Key and Non-Primary Key tables: #
AWS DMS will use SQL server’s native transaction replication method to capture the changes and replicate it to the Target. For non-primary key tables, AWS DMS will use MS-CDC feature to capture the changes.
How to enable CDC on RDS SQL Server: #
As per AWS blog,
Enable CDC feature for a particular Database
exec msdb.dbo.rds_cdc_enable_db 'db_name'Run the following for each table to enable MS-CDC:
exec sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = N'schema_name',
@source_name = N'table_name',
@role_name = NULL,
@supports_net_changes = 1 --for PK table 1, non PK tables 0
GOSet the retention period for the CDC data(in seconds):
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_change_job @job_type = 'capture' ,@pollinginterval = 86400What are all the difficulties here? #
- We have to run the *sp_cdc_enable_table * procedure on all the existing tables. If we have 500 table then we have to execute this procedure for 500 times.
- supports_net_changes – If the table has a primary key then we have to use 1, for non-primary key tables use 0.
- Manually execute the sp_cdc_enable_table after a table has been created. Before adding this table to CDC, DMS won’t replicate the data. So we must have to enable CDC before inserting any data in it.
- Multi-AZ won’t have CDC: In case if the RDS failover to the standby instance, then the CDC setting are won’t replicate. AWS recommends to use rds_set_configuration. But I’ll research and update later.
How did I fix these three difficulties? #
I have written a stored procedure to automatically enables CDC on the existing tables. It’ll get the list of tables from the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES and compare it with INFORMATION_SCHEMA.CONSTRAINTS. So if the table has Primary key and it’ll pass 1 to the supports_net_changes else it will pass 0.
Enable CDC on existing tables in one- shot: #
Install the below procedure on the database where you need to enable CDC.
/*****************************************************************
-------------------------------------
tsqltools - RDS Add CDC
-------------------------------------
Description: This stored procedure will help you to enable CDC on
all the exsiting tables. You have to run this store procedure on the
database where you need to add the tables. It won't support Cross
database's tables.
How to Run: If you want to enable CDC on the tables which
all are in DBAdmin database,
USE DBAdmin
GO
EXEC sp_add_cdc 'DBAdmin'
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Version: v1.0
Release Date: 2018-02-09
Author: Bhuvanesh(@BhuviTheDataGuy)
License: GPL-3.0
tsqltools is free to download.It contains Tsql stored procedures
and scripts to help the DBAs and Developers to make job easier
(C) 2017
*******************************************************************/
-- READ THE DESCRIPTION BEFORE EXECUTE THIS ***
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.sp_add_cdc') IS NULL
EXEC ('CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.sp_add_cdc AS RETURN 0;');
GO
ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_add_cdc]
@cdcdbname NVARCHAR(100)
as begin
exec msdb.dbo.rds_cdc_enable_db @cdcdbname
DECLARE @name VARCHAR(50)
-- For PrimaryKey Tables
DECLARE primary_tbl_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT t1.table_name
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES t1
Join INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS t2 on t1.TABLE_NAME=t2.TABLE_NAME
Join sys.tables t3 on t1.table_name = t3.name
WHERE t1.TABLE_TYPE='BASE TABLE' and t2.CONSTRAINT_TYPE='PRIMARY KEY' and t1.table_schema !='cdc' and t3.is_tracked_by_cdc=0;
OPEN primary_tbl_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM primary_tbl_cursor INTO @name
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
declare @primary int = 1
declare @p_schema nvarchar(100)=(select table_schema
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
where TABLE_NAME=@name)
declare @p_tbl nvarchar(100)=(select table_name
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
where TABLE_NAME=@name)
exec sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = @p_schema,
@source_name = @p_tbl,
@role_name = NULL,
@supports_net_changes = @primary
FETCH NEXT FROM primary_tbl_cursor INTO @name
END
CLOSE primary_tbl_cursor
DEALLOCATE primary_tbl_cursor
-- For Non-PrimaryKey Tables
DECLARE nonprimary_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT table_name
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES Join sys.tables t3 on table_name = t3.name
where TABLE_NAME not in (select table_name
from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS) and table_schema !='cdc' and TABLE_NAME !='systranschemas' and t3.is_tracked_by_cdc=0;
OPEN nonprimary_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM nonprimary_cursor INTO @name
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
declare @n_primary int = 0
declare @n_schema nvarchar(100)=(select table_schema
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
where TABLE_NAME=@name)
declare @n_tbl nvarchar(100)=(select table_name
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
where TABLE_NAME=@name)
exec sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = @n_schema,
@source_name = @n_tbl,
@role_name = NULL,
@supports_net_changes = @n_primary
FETCH NEXT FROM nonprimary_cursor INTO @name
END
CLOSE nonprimary_cursor
DEALLOCATE nonprimary_cursor
ENDIn this example, I have enabled CDC on DBAdmin database.
EXEC sp_add_cdc 'DBAdmin'Automatically enable CDC on newly created tables: #
For this, I have created a database trigger which will execute the sp_cdc_enable_table procedure once the table has been created. Once the table has been created then this trigger get the table schema and name from the EventData() and store it into the DBSchema_Change_Log table(We have to create this table before creating the trigger). Then it’ll get the schema name, table name, is primary key or not. Then it’ll pass the parameters to sp_cdc_enable_table .
Run the below procedure to create Triggers also track new tables and add the trigger automatically.
/*****************************************************************
-------------------------------------
tsqltools - RDS - Auto CDC
-------------------------------------
Description: This stored procedure will help you to enable CDC
automatically when a tables is created. This is basically a database
Trigger and it'll ecxecute enable CDC procedure when we creat a
new table. This is a database level trigger, so it won't replicate
the new tables which are in another database.
How to Run: If you to enable this on DBAdmin database,
USE DBAdmin
GO
-- Execute the below Query.
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Version: v1.0
Release Date: 2018-02-10
Author: Bhuvanesh(@BhuviTheDataGuy)
License: GPL-3.0
tsqltools is free to download.It contains Tsql stored procedures
and scripts to help the DBAs and Developers to make job easier
(C) 2018
*******************************************************************/
-- READ THE DESCRIPTION BEFORE EXECUTE THIS ***
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[DBSchema_Change_Log]
(
[RecordId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[EventTime] [datetime] NULL,
[LoginName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[UserName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[DatabaseName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[SchemaName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[ObjectName] [varchar](50) NULL,
[ObjectType] [varchar](50) NULL,
[DDLCommand] [varchar](max) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
CREATE TRIGGER [auto_cdc] ON Database
FOR CREATE_TABLE
AS
DECLARE @eventInfo XML
SET @eventInfo = EVENTDATA()
INSERT INTO DBSchema_Change_Log
VALUES
(
REPLACE(CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/PostTime)')),'T', ' '),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/LoginName)')),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/UserName)')),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/DatabaseName)')),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/SchemaName)')),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/ObjectName)')),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(50),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/ObjectType)')),
CONVERT(VARCHAR(MAX),@eventInfo.query('data(/EVENT_INSTANCE/TSQLCommand/CommandText)'))
)
declare @tbl varchar(100) =(select top(1)
OBJECTname
from DBSchema_Change_Log
order by recordid desc)
DECLARE @schemaname varchar(100) =(select top(1)
schemaname
from DBSchema_Change_Log
order by recordid desc)
DECLARE @primarykey int =( select case CONSTRAINT_TYPE when 'PRIMARY KEY' THen 1 else 0 end as PRIMARYkey
from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS
where TABLE_NAME=@tbl and TABLE_SCHEMA=@schemaname)
exec sys.sp_cdc_enable_table
@source_schema = @schemaname,
@source_name = @tbl,
@role_name = NULL,
@supports_net_changes = @primarykey
GO
--Enable the Trigger
ENABLE TRIGGER [auto_cdc] ON database
GOThis store procedure and the trigger saved me a lot of time, So hopefully this will help if you are using RDS SQL Server with DMS for ongoing replication.
Limitations of the DMS on RDS SQL Server: #
- It won’t replicate the following things.
- Foreign key
- Index
- trigger
- functions
- stored procedure
- Constraints
- Initially, we have a execute a command to enable CDC for each and every table. (We have a solution for this)
- It won’t add newly created tables to replication(we have the solution)
- If Multi-AZ enabled, then the Secondary server won’t have the CDC information(Again we have to manually enable CDC, this might be lead to some data loss during multi AZ failover – I’ll work to overcome this).
To learn more about the limitations, refer this AWS Documentation.