Build Production Grade Debezium Cluster With Confluent Kafka
We are living in the DataLake world. Now almost every organizations wants their reporting in Near Real Time. Kafka is of the best streaming platform for realtime reporting. Based on the Kafka connector, RedHat designed the Debezium which is an OpenSource product and high recommended for real time CDC from transnational databases. I referred many blogs to setup this cluster. But I found just basic installation steps. So I setup this cluster for AWS with Production grade and publishing this blog.
A shot intro: #
Debezium is a set of distributed services to capture changes in your databases so that your applications can see those changes and respond to them. Debezium records all row-level changes within each database table in a change event stream, and applications simply read these streams to see the change events in the same order in which they occurred.
Basic Tech Terms: #
- Kafka Broker: Brokers are the core for the kafka streaming, they’ll keep your messages and giving it to the consumers.
- Zookeeper: It’ll maintain the cluster status and node status. It’ll help to make the Kafka’s availability.
- Producers: The component who will send the messages(data) to the Broker.
- Consumers: The component who will get the messages from the Queue for further analytics.
- Confluent: Confluent is having their own steaming platform which basically using Apache Kafka under the hood. But it has more features.
Here Debezium is our data producer and S3sink is our consumer. For this setup, Im going to stream the MySQL data changes to S3 with customized format.
AWS Architecture: #
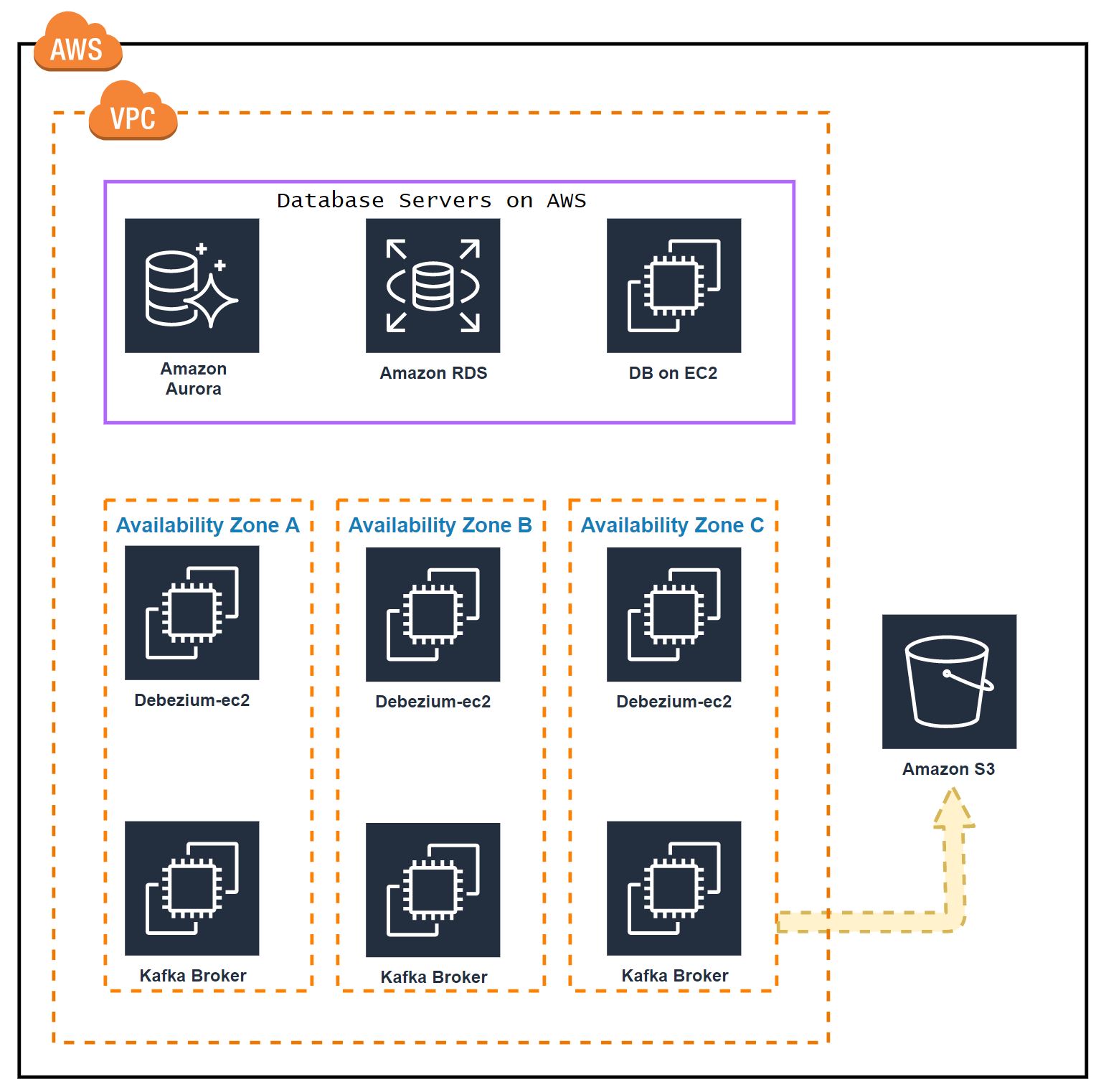
Kafka and Zookeepers are installed on the same EC2. We we’ll deploy 3 node confluent Kafka cluster. Each node will be in a different availability zone.
- 172.31.47.152 - Zone A
- 172.31.38.158 - Zone B
- 172.31.46.207 - Zone C
For Producer(debezium) and Consumer(S3sink) will be hosted on the same Ec2. We’ll 3 nodes for this.
- 172.31.47.12 - Zone A
- 172.31.38.183 - Zone B
- 172.31.46.136 - Zone C
Instance Type: #
Kafka nodes are generally needs Memory and Network Optimized. You can choose either Persistent and ephemeral storage. I prefer Persistent SSD Disks for Kafka storage. So add n GB size disk to your Kafka broker nodes. For Normal work loads its better to go with R5 instance Family.
Mount the Volume in /kafkadata location.
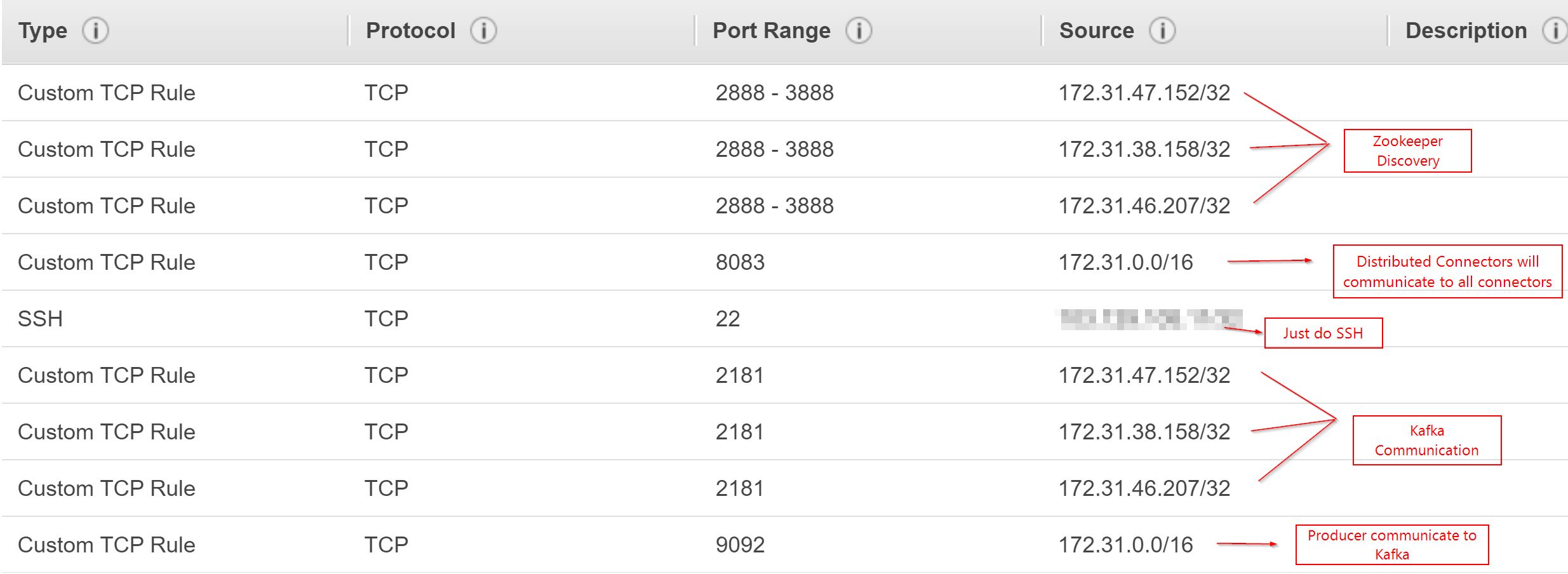
Security Group: #
Use a new Security group which allows the below ports.
Installation: #
Install the Java and Kafka on all the Broker nodes.
-- Install OpenJDK
apt-get -y update
sudo apt-get -y install default-jre
-- Install Confluent Kafka platform
wget -qO - https://packages.confluent.io/deb/5.3/archive.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.confluent.io/deb/5.3 stable main"
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install confluent-platform-2.12Configuration: #
We need to configure Zookeeper and Kafaka properties, Edit the /etc/kafka/zookeeper.properties on all the kafka nodes
-- On Node 1
dataDir=/var/lib/zookeeper
clientPort=2181
maxClientCnxns=0
server.1=0.0.0.0:2888:3888
server.2=172.31.38.158:2888:3888
server.3=172.31.46.207:2888:3888
autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
autopurge.purgeInterval=24
initLimit=5
syncLimit=2
-- On Node 2
dataDir=/var/lib/zookeeper
clientPort=2181
maxClientCnxns=0
server.1=172.31.47.152:2888:3888
server.2=0.0.0.0:2888:3888
server.3=172.31.46.207:2888:3888
autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
autopurge.purgeInterval=24
initLimit=5
syncLimit=2
-- On Node 3
dataDir=/var/lib/zookeeper
clientPort=2181
maxClientCnxns=0
server.1=172.31.47.152:2888:3888
server.2=172.31.38.158:2888:3888
server.3=0.0.0.0:2888:3888
autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
autopurge.purgeInterval=24
initLimit=5
syncLimit=2We need to assign a unique ID for all the Zookeeper nodes.
-- On Node 1
echo "1" > /var/lib/zookeeper/myid
--On Node 2
echo "2" > /var/lib/zookeeper/myid
--On Node 3
echo "3" > /var/lib/zookeeper/myidNow we need to configure Kafka broker. So edit the /etc/kafka/server.properties on all the kafka nodes.
--On Node 1
broker.id.generation.enable=true
delete.topic.enable=true
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
zookeeper.connect=172.31.47.152:2181,172.31.38.158:2181,172.31.46.207:2181
log.dirs=/kafkadata/kafka
log.retention.hours=168
num.partitions=1
--On Node 2
broker.id.generation.enable=true
delete.topic.enable=true
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
log.dirs=/kafkadata/kafka
zookeeper.connect=172.31.47.152:2181,172.31.38.158:2181,172.31.46.207:2181
log.retention.hours=168
num.partitions=1
-- On Node 3
broker.id.generation.enable=true
delete.topic.enable=true
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
log.dirs=/kafkadata/kafka
zookeeper.connect=172.31.47.152:2181,172.31.38.158:2181,172.31.46.207:2181
num.partitions=1
log.retention.hours=168The next step is optimizing the Java JVM Heap size, In many places kafka will go down due to the less heap size. So Im allocating 50% of the Memory to Heap. But make sure more Heap size also bad. Please refer some documentation to set this value for very heavy systems.
vi /usr/bin/kafka-server-start
export KAFKA_HEAP_OPTS="-Xmx2G -Xms2G"The another major problem in the kafka system is the open file descriptors. So we need to allow the kafka to open at least up to 100000 files.
vi /etc/pam.d/common-session
session required pam_limits.so
vi /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 10000
* hard nofile 100000
cp-kafka soft nofile 10000
cp-kafka hard nofile 100000Here the cp-kafka is the default user for the kafka process.
Create Kafka data dir: #
mkdir -p /kafkadata/kafka
chown -R cp-kafka:confluent /kafkadata/kafka
chmode 710 /kafkadata/kafkaStart the Kafka cluster: #
sudo systemctl start confluent-zookeeper
sudo systemctl start confluent-kafka
sudo systemctl start confluent-schema-registryMake sure the Kafka has to automatically starts after the Ec2 restart.
sudo systemctl enable confluent-zookeeper
sudo systemctl enable confluent-kafka
sudo systemctl enable confluent-schema-registryNow our kafka cluster is ready. To check the list of system topics run the following command.
kafka-topics --list --zookeeper localhost:2181
__confluent.support.metricsSetup Debezium: #
Install the confluent connector and debezium MySQL connector on all the producer nodes.
apt-get update
sudo apt-get install default-jre
wget -qO - https://packages.confluent.io/deb/5.3/archive.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.confluent.io/deb/5.3 stable main"
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install confluent-hub-client confluent-common confluent-kafka-connect-s3 confluent-kafka-2.12Configuration: #
Edit the /etc/kafka/connect-distributed.properties on all the producer nodes to make our producer will run on a distributed manner.
-- On all the connector nodes
bootstrap.servers=172.31.47.152:9092,172.31.38.158:9092,172.31.46.207:9092
group.id=debezium-cluster
plugin.path=/usr/share/java,/usr/share/confluent-hub-componentsInstall Debezium MySQL Connector: #
confluent-hub install debezium/debezium-connector-mysql:latestit’ll ask for making some changes just select Y for everything.
Run the distributed connector as a service: #
vi /lib/systemd/system/confluent-connect-distributed.service
[Unit]
Description=Apache Kafka - connect-distributed
Documentation=http://docs.confluent.io/
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=cp-kafka
Group=confluent
ExecStart=/usr/bin/connect-distributed /etc/kafka/connect-distributed.properties
TimeoutStopSec=180
Restart=no
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetStart the Service: #
systemctl enable confluent-connect-distributed
systemctl start confluent-connect-distributedConfigure Debezium MySQL Connector: #
Create a mysql.json file which contains the MySQL information and other formatting options.
{
"name": "mysql-connector-db01",
"config": {
"name": "mysql-connector-db01",
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnector",
"database.server.id": "1",
"tasks.max": "3",
"database.history.kafka.bootstrap.servers": "172.31.47.152:9092,172.31.38.158:9092,172.31.46.207:9092",
"database.history.kafka.topic": "schema-changes.mysql",
"database.server.name": "mysql-db01",
"database.hostname": "172.31.84.129",
"database.port": "3306",
"database.user": "bhuvi",
"database.password": "my_stong_password",
"database.whitelist": "proddb,test",
"internal.key.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"key.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"internal.key.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"internal.value.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"value.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"internal.value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"key.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"transforms": "unwrap",
"transforms.unwrap.type": "io.debezium.transforms.ExtractNewRecordState",
"transforms.unwrap.add.source.fields": "ts_ms",
"tombstones.on.delete": false
}
}- “database.history.kafka.bootstrap.servers” - Kafka Servers IP.
- “database.whitelist” - List of databases to get the CDC.
- key.converter and value.converter and transforms parameters - By default Debezium output will have more detailed information. But I don’t want all of those information. Im only interested in to get the new row and the timestamp when its inserted.
If you don’t want to customize anythings then just remove everything after the database.whitelist
Register the MySQL Connector: #
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8083/connectors -d @mysql.jsonCheck the status: #
curl GET localhost:8083/connectors/mysql-connector-db01/status
{
"name": "mysql-connector-db01",
"connector": {
"state": "RUNNING",
"worker_id": "172.31.94.191:8083"
},
"tasks": [
{
"id": 0,
"state": "RUNNING",
"worker_id": "172.31.94.191:8083"
}
],
"type": "source"
}Test the MySQL Consumer: #
Now insert something into any tables in proddb or test (because we have whilelisted only these databaes to capture the CDC.
use test;
create table rohi (id int,
fn varchar(10),
ln varchar(10),
phone int );
insert into rohi values (2, 'rohit', 'ayare','87611');We can get these values from the Kafker brokers. Open any one the kafka node and run the below command.
I prefer confluent cli for this. By default it’ll not be available, so download manually.
curl -L https://cnfl.io/cli | sh -s -- -b /usr/bin/Listen the below topic: #
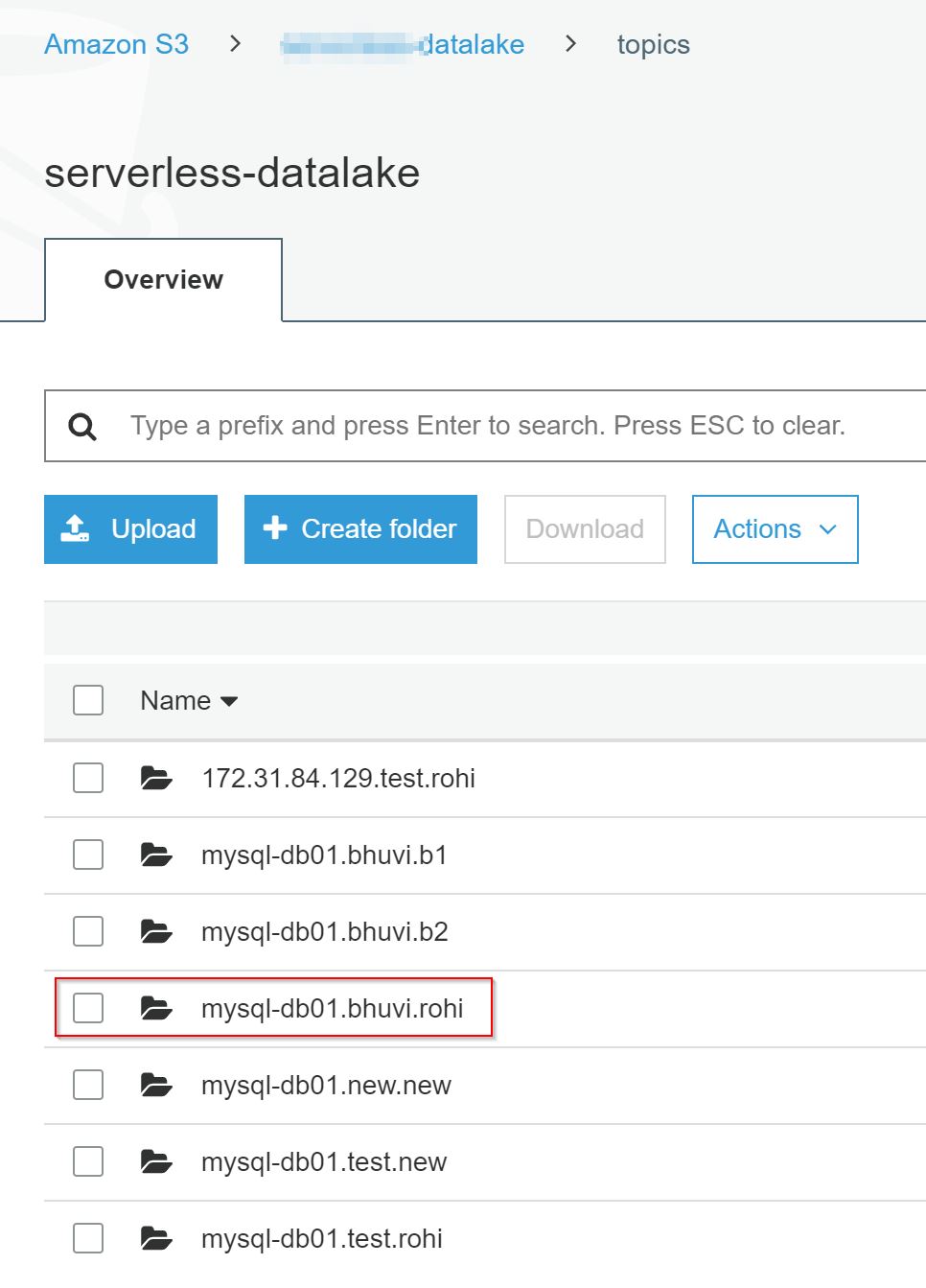
mysql-db01.test.rohi
This is the combination ofservername.databasename.tablename
servername(you mentioned this in as a server name in mysql json file).
confluent local consume mysql-db01.test.rohi
----
The local commands are intended for a single-node development environment
only, NOT for production usage. https://docs.confluent.io/current/cli/index.html
-----
{"id":1,"fn":"rohit","ln":"ayare","phone":87611,"__ts_ms":1576757407000}Setup S3 Sink connector in All Producer Nodes: #
I want to send this data to S3 bucket. So you must have an EC2 IAM role which has access to the target S3 bucket. Or install awscli and configure access and secret key(but its not recommended)
Install S3 Connector: #
confluent-hub install confluentinc/kafka-connect-s3:latestCreate s3.json file.
{
"name": "s3-sink-db01",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.s3.S3SinkConnector",
"storage.class": "io.confluent.connect.s3.storage.S3Storage",
"s3.bucket.name": "bhuvi-datalake",
"name": "s3-sink-db01",
"tasks.max": "3",
"s3.region": "us-east-1",
"s3.part.size": "5242880",
"s3.compression.type": "gzip",
"timezone": "UTC",
"locale": "en",
"flush.size": "10000",
"rotate.interval.ms": "3600000",
"topics.regex": "mysql-db01.(.*)",
"internal.key.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"key.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"internal.key.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"format.class": "io.confluent.connect.s3.format.json.JsonFormat",
"internal.value.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"value.converter.schemas.enable": "false",
"internal.value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"key.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter",
"partitioner.class": "io.confluent.connect.storage.partitioner.HourlyPartitioner",
"path.format": "YYYY/MM/dd/HH",
"partition.duration.ms": "3600000",
"rotate.schedule.interval.ms": "3600000"
}
}"topics.regex": "mysql-db01"- It’ll send the data only from the topics which hasmysql-db01as prefix. In our case all the MySQL databases related topics will start with this prefix."flush.size"- The data will uploaded to S3 only after these many number of records stored. Or after"rotate.schedule.interval.ms"this duration.
Register this S3 sink connector: #
curl -X POST -H "Accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:8083/connectors -d @s3Check the Status: #
curl GET localhost:8083/connectors/s3-sink-db01/status
{
"name": "s3-sink-db01",
"connector": {
"state": "RUNNING",
"worker_id": "172.31.94.191:8083"
},
"tasks": [
{
"id": 0,
"state": "RUNNING",
"worker_id": "172.31.94.191:8083"
},
{
"id": 1,
"state": "RUNNING",
"worker_id": "172.31.94.191:8083"
},
{
"id": 2,
"state": "RUNNING",
"worker_id": "172.31.94.191:8083"
}
],
"type": "sink"
}Test the S3 sync: #
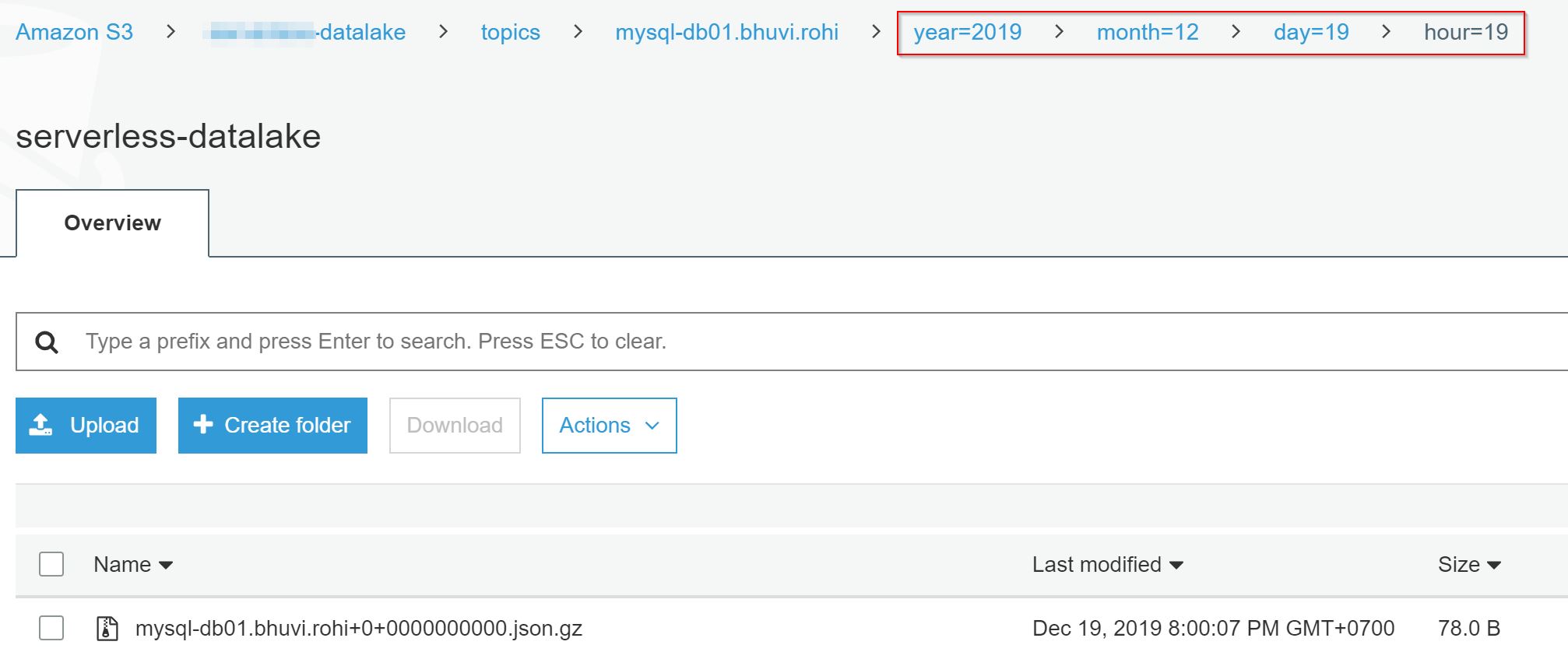
Insert the 10000 rows into the rohi table. Then check the S3 bucket. It’ll save the data in JSON format with GZIP compression. Also in a HOUR wise partitions.
Monitoring: #
Refer this post to setup monitoring for MySQL Connector.
More Tuning: #
- Replication Factor is the other main parameter to the data durability.
- Use internal IP addresses as much as you can.
- By default debezium uses 1 Partition per topic. You can configure this based on your work load. But more partitions more through put needed.
References: #
- Setup Kafka in production by confluent
- How to choose number of partition
- Open file descriptors for Kafka
- Kafka best practices in AWS
- Debezium documentation
- Customize debezium output with SMT
Debezium Series blogs: #
- Build Production Grade Debezium Cluster With Confluent Kafka
- Monitor Debezium MySQL Connector With Prometheus And Grafana
- Debezium MySQL Snapshot From Read Replica With GTID
- Debezium MySQL Snapshot From Read Replica And Resume From Master
- Debezium MySQL Snapshot For AWS RDS Aurora From Backup Snaphot
- RealTime CDC From MySQL Using AWS MSK With Debezium