MySQL With DevOps 1 - Automate Database Archive

This is my next blog series. Im going to write about how I automated many complex tasks in MySQL with Rundeck. In my last series, I have explained RunDeck basics. You can find those articles here. In this blog Im writing about how I automated MySQL archive for multiple tables in one Rundeck job.
Challeange with Replication: #
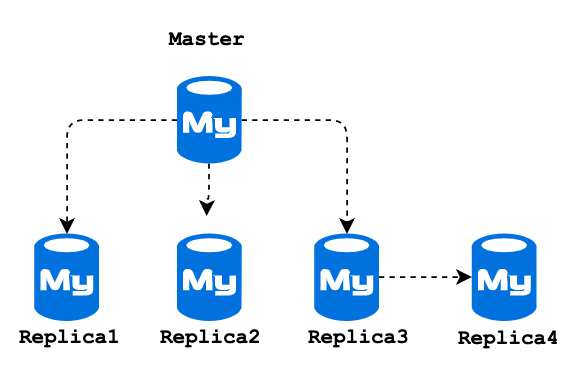
My MySQL database setup has 1 Master 4 Read Replica and the 3’rd replica is an intermediate Master for Replica 4. I don’t want to archive this data on Replica 3 and 4. Because these replicas are using for generating historical reports also some internal application.
Disable Log-Bin: #
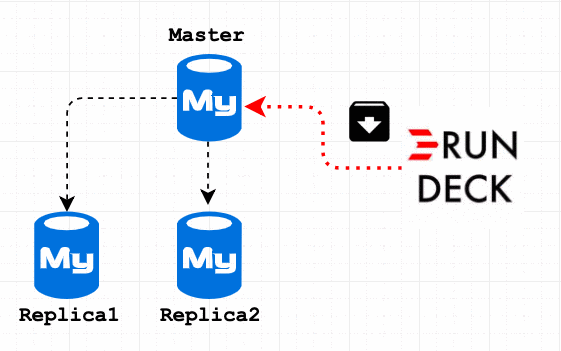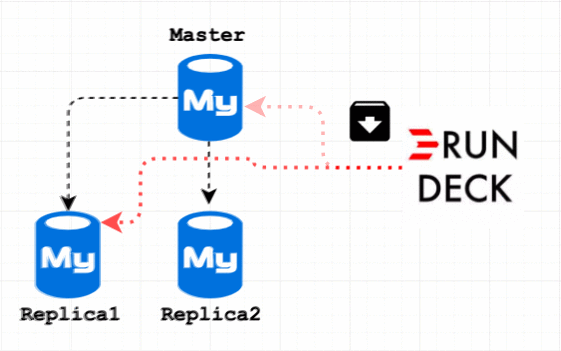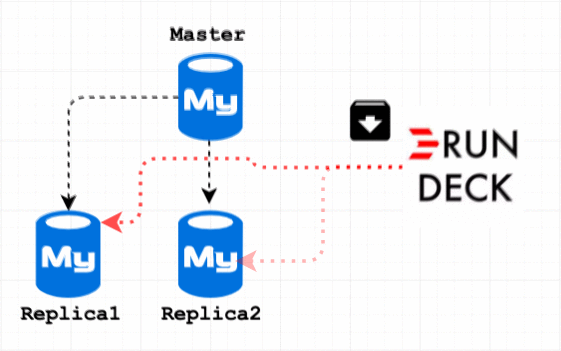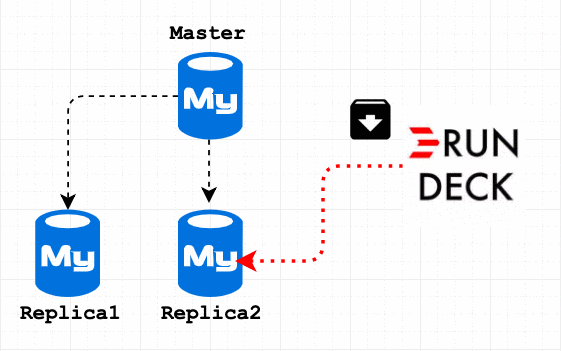
To prevent archive data on Replica 3 and 4, I decided to disable binlog on my archive session. But another challenge is, it won’t replicate to Replica 1 and 2. So my final solution is Archive the data on Master, then execute the archive scripts on Replica 1 and Replica 2.
Archive Condition: #
I have 50+ tables which need to be archived older than 30days records. Each table has a timestamp column. But the column name is different on all the tables. For few tables, I need to select older than 30days based on multiple columns.
Example: #
Delete from table_name where date_col < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month);
Delete from table_name where date_col < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month) AND date_col2 < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month);RunDeck Options: #
To securely pass MySQL password in shell script we are going to use RunDeck key storage. Read here how to save the password in Rundeck.
Process Flow: #
The job should follow the below steps and whenever a step failed, then stop executing further steps.
- Table dump with where clause (we are removing older than 30days data, so dump those 30days data).
- Sync the Dump files to cloud storage(here my complete infra in GCP).
- Restore the dump on Archive DB Server.
- Delete the records on Master.
- Delete the records on Replica 1.
- Delete the records on Replica 2.
Lets create the automation job.
Table name and Column names: #
Create a file /opt/rundeckfiles/archive_tables.txt contains table name and columns. We need to mention the table and use a comma to separate column names. The file structure would be,
table_name1,column1
table_name2,column1,column2
table_name3,column1Stored procedure to delete in chunks: #
I have written a blog on how to perform archive operation in the right way. You can read it here. So we are going to delete this data with 1000 rows per chunk. Im maintaining DBA related functions and procedures in a separate database called dbadmin
##Note
My database server has only one master db and going to archive this particular database. So in the procedure, I have mentioned my database name. Also, I used SET sql_log_bin =OFF; because I don’t want to replica it to Replica 3 and 4. So if your use case is just archive on all the servers you can remove this line.
DROP PROCEDURE
IF EXISTS archive_tables;
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE
archive_tables(IN delete_query varchar(500))
begin
DECLARE rows INT;
SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ COMMITTED;
SET sql_log_bin =OFF;
SET rows = 1;
WHILE rows > 0
do
SET autocommit=1;
SET @query =CONCAT('DELETE FROM DBname.',delete_query,' LIMIT 10000;');
select @query;
PREPARE arcive_stmt FROM @query;
EXECUTE arcive_stmt;
SET rows = row_count();
select sleep(1);
commit;
DEALLOCATE PREPARE arcive_stmt;
END WHILE;
END //
delimiter ; The above procedure will get the where clause from the shell script and prepare the complete delete statement.
Grab Table name & Column name from the file: #
Shell script should get the first value from the file as table and rest of the values are column names in a line. So we need to separate this table and column names with comma.
# $line means read the complete line from the text file
#Get the first value as table name:
table_name=`echo $line | awk -F',' '{print $1}'`
#Generate the where clause for archive:
archive_query=`echo $line |sed 's/,/ where /' |awk -F ',' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`
#Generate the where clause for dump:
dump_command=`echo $line |awk -F, '{$1=""; print}' |awk -F ' ' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`Example: #
To understand this process in more detail, Im giving an example. For executing archive stored procedure it should generate the delete_query with table and where clause. For dump we just generate the where clause alone.
[root@sqladmin]# line='table_name,col1,col2'
[root@sqladmin]# table_name=`echo $line | awk -F',' '{print $1}'`
[root@sqladmin]# archive_query=`echo $line |sed 's/,/ where /' |awk -F ',' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`
[root@sqladmin]# dump_command=`echo $line |awk -F, '{$1=""; print}' |awk -F ' ' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`See the output: #
[root@sqladmin]# echo $archive_query
table_name where col1 < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month) and col2 < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)
[root@sqladmin]# echo $dump_command
col1 < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 3 month) and col2 < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)
[root@sqladmin]# Setup the Rundeck job: #
- Go to Jobs –> Create Job.
- Give a name for this job.
- In the Options, add option.
- Option Name: sqladmin-secret
- Option Label: SQLadmin-Secret
- Input Type: Secure –> Select the mysql password from key storage.
- Go to Workflow –> Add step.
The complete process will be running from Rundeck server itself. It’ll use -hto talk to DB servers.
My archive flow is to archive Master first and Replica1, 2. If your use case is just archive it on all the servers, then you must SET sql_log_bin =OFF; in the archive procedure. And in step 3 add the step for Master IP address. Step 4 would be Delete old dump(See Step 6)
Step 1: Dump the Data & Upload to GCS Bucket #
set -e
set -u
#Password
[email protected]@
#Parameters for Dump Path
DATE=`date +%Y%m%d`
gcs_folder=`date +%Y-%m-%d`
dump_path=/data/my_db/$gcs_folder
mkdir -p /data/my_db/$gcs_folder
while read line
do
table_name=`echo $line | awk -F',' '{print $1}'`
archive_query=`echo $line |sed 's/,/ where /' |awk -F ',' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`
dump_command=`echo $line |awk -F, '{$1=""; print}' |awk -F ' ' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`
mysqldump -h 10.0.0.1 -u admin -p$secret --set-gtid-purged=OFF --single-transaction my_db -t $table_name --where "$dump_command" > $dump_path/$table_name.$DATE.sql
/bin/gsutil cp $dump_path/$table_name.$DATE.sql gs://bucket-name/my_db/$gcs_folder/
done < /opt/rundeckfiles/archive_tables.txt Here my backup files are upload to GCS bucket with current date’s folder. You can use AWS Cli, if you want to use it in AWS. Change the IP address of MySQL Master or if you want to take dump from slave use Slave IP in -h
Step 2: Restore the dump files to Archive DB: #
Please use a separate db server for archive data. Restore the schema on the db server. Change the IP address of archive DB.
set -e
set -u
#mysql secret
[email protected]@
#restore dump to archive db
gcs_folder=`date +%Y-%m-%d`
dump_path=/data/my_db/$gcs_folder
for i in $dump_path/*.sql
do
echo "importing $i"
mysql -h 10.0.0.10 -u admin -p$secret db_name < $i
doneStep 3,4,5 : Archive it on Master/Replica1/Replica2: #
set -e
set -u
#password
[email protected]@
#archive master
while read line
do
table_name=`echo $line | awk -F',' '{print $1}'`
echo "Deleteing $table_name"
archive_query=`echo $line |sed 's/,/ where /' |awk -F ',' -v OFS=',' -vsuf=" < DATE(Now() - INTERVAL 1 month)" '{ for (i=1;i<=NF;++i) $i = pre $i suf; print }' |sed 's/,/ and /g'`
mysql -h 10.0.0.1 -u admin -p$secret dbadmin -e"CALL archive_tables ('$archive_query');"
done < /opt/rundeckfiles/archive_tables.txtCopy the above script and use the same for step 4 and 5 but change the IP address of the MySQL server 10.0.0.1.
Step 6: delete older than 1day dumps: #
We don’t want to keep the dump files. So the last step will remove those dump files.
old_folder=`date --date="1 day ago" +%Y-%m-%d`
dump_path=/data/my_db/$old_folder
#delete yesterday's dump_path
rm -rf $dump_path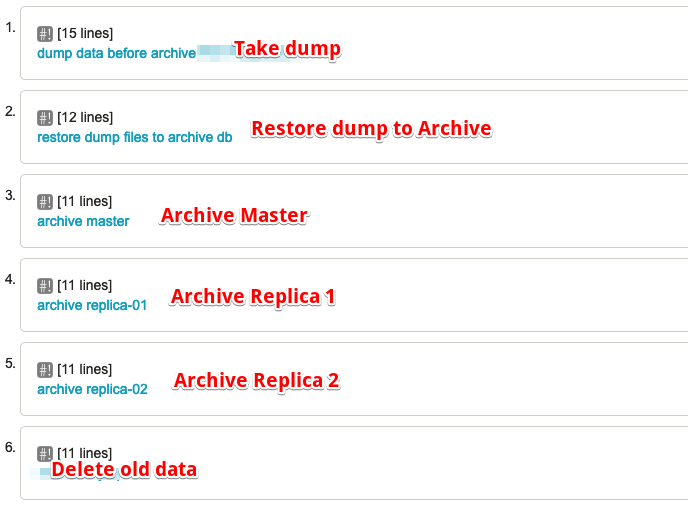
Add tables in future: #
If you want to add tables in future, just add the table name and archive where clause column name in the txt file.