RedShift Unload to S3 With Partitions - Stored Procedure Way
Redshift unload is the fastest way to export the data from Redshift cluster. In BigData world, generally people use the data in S3 for DataLake. So its important that we need to make sure the data in S3 should be partitioned. So we can use Athena, RedShift Spectrum or EMR External tables to access that data in an optimized way. If you are dealing with multiple tables, then you can loop the table names in a shell script or Python code. But as a SQL guy, I choose stored procedures to do this. It made export process simple.
In this procedure I just used the options which are suitable for me, but you can use the same procedure and do whatever customization you want. Also you can track the activity of this unload in a metadata table.
CREATE TABLE unload_meta (
id INT IDENTITY(1, 1)
,tablename VARCHAR(500)
,start_time DATETIME
,end_time DATETIME
,export_query VARCHAR(65500)
);Define the parameters:
starttime- timestamp when the process startedendtime- timestamp when the process endsql- SQL Query that you want to export its results to S3.s3_path- location of S3 with prefix. Make sure you have end this string with/.iamrole- IAM role ARN which has s3 write access.delimiter- If you are exporting as CSV, you can define your delimiter.un_year- Partition YEARun_month- Partition MONTHun_day- Partition DAY
In this procedure, I used GETDATE() function to pass current day, month, year into partition variables. If you want custom one, you can get these variables from input in stored procedure.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE sp_unload(v_tablename varchar)
LANGUAGE plpgsql AS
$$
DECLARE
starttime datetime;
endtime datetime;
sql text;
s3_path varchar(1000);
iamrole varchar(100);
delimiter varchar(10);
unload_query text;
max_filesize varchar(100);
un_year int;
un_month int;
un_day int;
BEGIN
select extract(year from GETDATE()) into un_year;
select extract(month from GETDATE()) into un_month;
select extract(day from GETDATE()) into un_day;
select GETDATE() into starttime;
sql:='select * from '||v_tablename||'' ;
s3_path:='s3://bhuvi-datalake/clicksteam/';
iamrole:='arn:aws:iam::123123123123:role/myredshiftrole';
delimiter:='|';
unload_query := 'unload ('''||sql||''') to '''||s3_path||un_year||'/'||un_month||'/'||un_day||'/'||v_tablename||'_'' iam_role '''||iamrole||''' delimiter '''||delimiter||''' MAXFILESIZE 100 MB PARALLEL ADDQUOTES HEADER GZIP';
execute unload_query;
select GETDATE() into endtime;
Insert into unload_meta (tablename, start_time, end_time, export_query) values (v_tablename,starttime,endtime,unload_query);
END
$$; Here, Im getting the table name from input. Then I used multiple options like parallel, max file size, include headers and compress. If you don’t want to use this, you can remove these options from the unload_query. Also if you need you can get the s3 location and other parameters from the user input. You can do many customization here.
Lets try this.
test=# call sp_unload('bhuvi');
INFO: UNLOAD completed, 400000 record(s) unloaded successfully.
CALL
test=#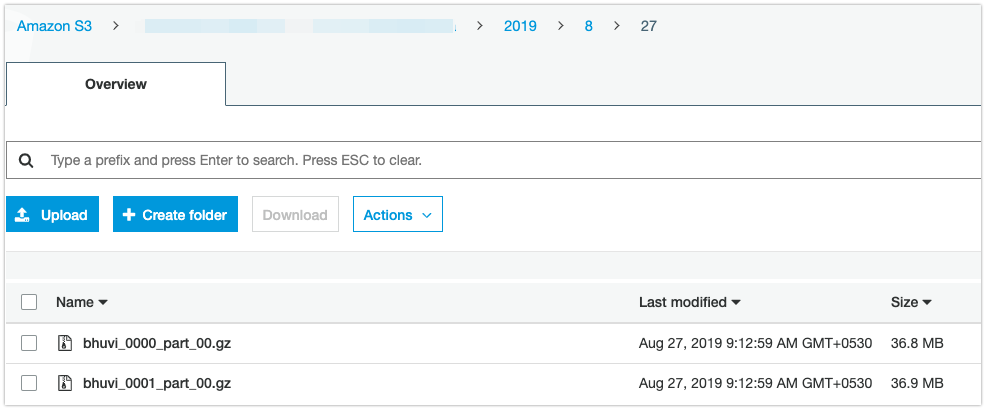
Get the unload History from Meta table:
select * from unload_meta;
id | 1
tablename | bhuvi
start_time | 2019-08-27 03:42:57
end_time | 2019-08-27 03:43:03
export_query | unload ('select * from bhuvi') to 's3://bhuvi-datalake/clicksteam/2019/8/27/bhuvi_' iam_role 'arn:aws:iam::123123123:role/myredshiftrole' delimiter '|' MAXFILESIZE 100 MB PARALLEL ADDQUOTES HEADER GZIP
In my next blog, I’ll write about how to automate this Unload Process in AWS Glue and convert the CSV to Parquet format.
Update: #
I have written the updated version of this stored procedure to unload all of the tables in a database to S3. You can read it here: https://thedataguy.in/redshift-unload-all-tables-to-s3/